Bursitis Foot Pads
Whenever tissues rub against one another, a bursa forms to allow for smooth gliding. A bursa is a fluid-filled sac and occurs normally throughout the body. Only a few cell layers thick, a bursa is filled with a lubricating fluid. However, when irritated, a bursa can become markedly thickened and painful. This is often referred to as bursitis. The retrocalcaneal bursa is positioned to allow the Achilles tendon to glide over the back part (posterior aspect) of the heel bone. When this bone becomes enlarged, inflammation of the retrocalcaneal bursa occurs. This inflammation results in exquisite tenderness along the posterior aspect of the heel.
Causes
The most common causes of bursitis are injury or overuse, although infection may also be a cause. Bursitis is also associated with other causes, such as arthritis, gout, tendinitis, diabetes, and thyroid disease.
Symptoms
Symptoms include pain at the back of the heel, especially when running uphill or on soft surfaces. There will be tenderness and swelling at the back of the heel which may make it difficult to wear certain shoes. When pressing in with the fingers both sides are the back of the heel a spongy resistance may be felt.
Diagnosis
When you are experiencing Achilles pain at the back of your heel, a visit to the doctor is always recommended. Getting a proper diagnosis is important so you can treat your condition correctly. A doctor visit is always recommended.
Non Surgical Treatment
For non-infectious bursitis, the preliminary treatment starts with non-operative options such as cold compression therapy and Blood Flow Stimulation Therapy. Surgery to remove the inflamed bursa is normally not required for bursitis, however if you fail to see improvement with the conservative treatments, your physician may recommend surgery to remove the bursa completely. Although this removes the problem of an inflamed bursa, you are left with less cushioning in your joint which can lead to a host of other conditions.
Surgical Treatment
Bursectomy is a surgical procedure used to remove an inflamed or infected bursa, which is a fluid-filled sac that reduces friction between tissues of the body. Because retrocalcaneal bursitis can cause chronic inflammation, pain and discomfort, bursectomy may be used as a treatment for the condition when it is persistent and cannot be relived with other treatments. During this procedure, a surgeon makes small incisions so that a camera may be inserted into the joint. This camera is called an arthroscope. Another small incision is made so that surgical instruments can be inserted to remove the inflamed bursa.
How To Treat Hammer Toes Without Surgery
 Overview
Overview
Hammer toe is defined as a deformity in the toe where part of the toe is permanently bent downward resembling a hammer. Two related conditions are mallet toe and claw toe which effect different toe joints in slightly different ways. The key difference is that hammertoe tends to effect the middle joint in the toe (note: not the middle toe, the middle toe joint). The disease is usually associated with the second largest toe but can effect the third or fourth toe as well. Mallet toe effects the uppermost toe joint whereas claw toe is caused by the tow being held in a cramped ?claw-like? position.
Causes
A common cause of hammertoe and mallet toe is wearing improper footwear - shoes that are too tight in the toe box, or high-heel shoes. Wearing shoes of either type can push your toes forward, crowding one or more of them into a space that's not large enough to allow your toes to lie flat. Hammertoe and mallet toe deformities can also be inherited and may occur despite wearing appropriate footwear. The result is a toe that bends upward in the middle and then curls down in a hammer-like or claw-like shape. Your shoes can rub against the raised portion of the toe or toes, causing painful corns or calluses. The bottom of the affected toe can press down, creating the mallet-like appearance of mallet toe. At first, a hammertoe or mallet toe may maintain its flexibility and lie flat when you're not wearing crowded footwear. But eventually, the tendons of the toe may contract and tighten, causing your toe to become permanently stiff.
 Symptoms
Symptoms
The most obvious symptom of hammer, claw or mallet toe is the abnormal toe position. This is usually combined with pain: the abnormal foot position leads to excessive friction on the toe as it rubs against any footwear which can be extremely painful. Corns & Calluses: repeated friction can result in the formation of a foot corn or callus on top of the toes. Stiffness, the joints become increasingly stiff. In the early stages, the toes can usually be straightened out passively using your hands, but if allowed to progress, the stiffness may be permanent.
Diagnosis
Hammertoes are progressive, they don?t go away by themselves and usually they will get worse over time. However, not all cases are alike, some hammertoes progress more rapidly than others. Once your foot and ankle surgeon has evaluated your hammertoes, a treatment plan can be developed that is suited to your needs.
Non Surgical Treatment
Pad it. Mild cases of hammertoe can be treated with corn pads or felt pads available in the pharmacy. Toe caps, the small, padded sleeves that fit around the tip of the toe, may relieve hammer toe pain. Change your shoes. Wear Hammer toe wide shoes with resilient soles. Avoid shoes with pointed toes. Exercise. Certain exercises such as moving and stretching your toe gently with your hands and picking small or soft objects such as marbles or towels can keep your toe joints flexible. Also, while you are watching television or reading, you can also put a towel flat under your feet and use your toes to crumple it. This simple exercise can stretch and strengthen your muscles. Use ice. If your hammer toe becomes painful, applying an ice pack several times a day can help relieve the soreness and swelling.
Take medications. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (also called NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or naproxen may be helpful in minimizing pain and inflammation. Use orthotic devices. Place a custom orthotic device in your shoe. This will help control the muscle/tendon imbalance.
Surgical Treatment
The deformity is corrected in a variety of ways. There are actually a large number of procedures. The simplest procedure would involve a Tenotomy, the cutting of the tendon causing the deformity or a Tendon Lengthening procedure. These procedures are infrequently done, though, as the structural deformity (the arthritis and joint adaptation) is not addressed with these surgeries. Other soft-tissue procedures involve rebalancing the tendons around the joint. There are several techniques to do this, but the most common is probably the Girdlestone-Taylor procedure, which involves rerouting the tendons on the bottom of the toe up and over the toe where it sticks up, so that the tendon helps pull the toe downwards into proper alignment.
 Prevention
Prevention
The best first step you can take is to evaluate your shoe choices. Ditch any shoes that aren?t serving your feet well. Shoes that crowd the front of your foot, especially around your toes, aggravate the existing condition and can also cause the condition to develop. If you suspect the development of hammertoe, you may also try using protective pads to prevent irritation and the development of corns. Custom orthotics to correct muscle imbalances in your feet may also help prevent hammertoe.
Hammer Toe Surgery Treatment
 Overview
Overview
Hammer toe is a type of crooked toe that involve unnatural contracture, or bending, of your toes. In most cases, a hammertoe is characterized by a toe malposition in which the end of your affected toe points down and the first joint of your same toe-your proximal interphalangeal joint-points up. This crooked toe syndrome usually leads to rubbing within your shoe and pain. A hammertoe resembles an upside-down letter v when viewed from the side. This crooked toe syndrome most commonly affects your second to fifth toes, though it may also affect your big toe. This health problem is more commonly experienced by women than men.
Causes
It is possible to be born with a hammer toe, however many people develop the deformity later in life. Common causes include tightened tendons that cause the toe to curl downward. Nerve injuries or problems with the spinal cord. Stubbing, jamming or breaking a toe. Having a stroke. Being a diabetic. Having a second toe that is longer than the big toe. Wearing high heels or tight shoes that crowd the toes and don?t allow them to lie flat. Aging.
 Symptoms
Symptoms
Well-developed hammertoes are distinctive due to the abnormal bent shape of the toe. However, there are many other common symptoms. Some symptoms may be present before the toe becomes overly bent or fixed in the contracted position. Often, before the toe becomes permanently contracted, there will be pain or irritation over the top of the toe, particularly over the joint. The symptoms are pronounced while wearing shoes due to the top of the toe rubbing against the upper portion of the shoe. Often, there is a significant amount of friction between the toe and the shoe or between the toe and the toes on either side of it. The corns may be soft or hard, depending on their location and age. The affected toe may also appear red with irritated skin. In more severe cases, blisters or open sores may form. Those with diabetes should take extra care if they develop any of these symptoms, as they could lead to further complications.
Diagnosis
Your doctor is very likely to be able to diagnose your hammertoe simply by examining your foot. Even before that, he or she will probably ask about your family and personal medical history and evaluate your gait as you walk and the types of shoes you wear. You'll be asked about your symptoms, when they started and when they hammertoes occur. You may also be asked to flex your toe so that your doctor can get an idea of your range of motion. He or she may order x-rays in order to better define your deformity.
Non Surgical Treatment
Symptomatic treatment of hammertoes consists of such things as open toed shoes or hammertoe pads. There are over the counter corn removers for temporally reducing the painful callous often seen with the hammertoe. These medications must be used with caution. They are a mild acid that burns the callous off. These medications should never be used for corns or callouses between the toes. Persons with diabetes or bad circulation should never use these products.
Surgical Treatment
Sometimes when the joints are removed the two bones become one as they are fused in a straightened position. Many times one toe will be longer than another and a piece of bone is removed to bring the toes in a more normal length in relation to each other. Sometimes tendons will be lengthened, or soft tissue around the joints will be cut or rebalanced to fix the deformity. Angular corrections may also be needed. The surgeon may place fixation in your foot as it heals which may include a pin, or wires.
 Prevention
Prevention
Prevention of a hammertoe can be difficult as symptoms do not arise until the problem exists. Wearing shoes that have extra room in the toes may eliminate the problem or slow down the deformity from getting worse. Sometimes surgery is recommended for the condition. If the area is irritated with redness, swelling, and pain some ice and anti-inflammatory medications may be helpful. The best prevention may be to get advice from your podiatrist.
Why Do I Get Bunions?
Overview
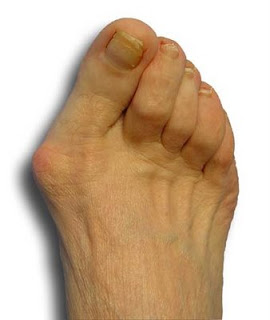 Bunion deformities are often part of a more generalized problem related to improper foot motion as you walk. The name for this is "pronation". Wearing orthotics can slow the progress of a bunion deformity. There are presently over 25 types of bunion procedures performed today. The choice of procedure is based on many factors including age, medical history, physical exam, and x-ray evaluation.
Bunion deformities are often part of a more generalized problem related to improper foot motion as you walk. The name for this is "pronation". Wearing orthotics can slow the progress of a bunion deformity. There are presently over 25 types of bunion procedures performed today. The choice of procedure is based on many factors including age, medical history, physical exam, and x-ray evaluation.
Causes
Perhaps the most frequent cause of bunion development is the wearing of shoes with tight, pointed toes, or with high heels that shift all of your body's weight onto your toes and also jam your toes into your shoes' toe boxes. It's estimated that more than 50 percent of women have bunions caused by high-heel shoes, and that nine out of 10 people who develop bunions are women. Bunions can also develop on your little toes, in which case they are called bunionettes or tailor's bunions.
Symptoms
The most common symptoms associated with this condition are pain on the side of the foot. Shoes will typically aggravate bunions. Stiff leather shoes or shoes with a tapered toe box are the prime offenders. This is why bunion pain is most common in women whose shoes have a pointed toe box. The bunion site will often be slightly swollen and red from the constant rubbing and irritation of a shoe. Occasionally, corns can develop between the 1st and 2nd toe from the pressure the toes rubbing against each other. On rare occasions, the joint itself can be acutely inflamed from the development of a sac of fluid over the bunion called a bursa. This is designed to protect and cushion the bone. However, it can become acutely inflamed, a condition referred to as bursitis.
Diagnosis
Orthopaedic surgeons diagnose bunions on the basis of physical examination and weight bearing x-rays. Two angles are assessed, the intermetatarsal angle, that is between the first and second metatarsals (the bones that lead up to the base of the toes). If this angle exceeds 9? (the angle found in the healthy foot) it is abnormal and referred to as metatarsus primus varus. the hallux valgus angle, that is, the angle of the big toe as it drifts toward the small toe. An angle that exceeds 15? is considered to be a sign of pathology.
Non Surgical Treatment
There are many treatment options for bunions and they will vary with the type and severity of each bunion and will also depend on what is causing the symptoms. Bunions are almost always progressive and tend to get larger and more painful with time, how fast this happens may be a function of the fit of the footwear. The initial goal of treatment options is to relieve pressure on the bunion and any symptoms that may be present and to halt or slow the progression of the joint deformity. There is no effective may be "get rid off" a bunion without surgery. There are a number of things that individuals and Podiatrists can do to help the symptoms and slow (if not halt) progression. 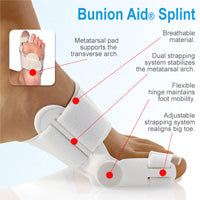
Surgical Treatment
Conservative bunion treatment methods help to reduce the symptoms but they cannot undo changes in the bone to fully correct the condition. If the pain becomes severe and it starts to affect your daily life, then foot bunion surgery may be the best option to correct a hallux abducto valgus. There are a number of different surgical options, depending on the severity of the bony deformity. The two most common types of surgery are Osteotomy. This is the most common type pf surgery and involves removing part of the bony lump and realigning the toes. It is also known as a bunionectomy or exostectomy. The ligaments around the big toe may also need realigning and this will be done at the same time if necessary. Fusion.This is where the joint at the base of the big toe (metatarsophalangeal joint) is fused together, known as an arthrodesis. This is only indicated in severe cases or if other treatments have failed as it severely limits the movement of the big toe.
Prevention
If these exercises cause pain, don't overdo them. Go as far as you can without causing pain that persists. This first exercise should not cause pain, but is great for stimulating blood and lymphatic circulation. Do it as often as you can every day. Only do this exercise after confirming it is OK with your doctor. Lie on your back and lift up your legs above you. Wiggle your toes and feet. Eventually you may be able to rapidly shake your feet for a minute at a time. Use your fingers to pull your big toe into proper alignment. Stretch your big toe and the rest of your toes. Curl them under for 10 seconds, then relax and let them point straight ahead for 10 seconds. Repeat several times. Do this at least once a day, and preferably several times. Flex your toes by pressing them against the floor or a wall until they are bent back. Hold them for 10 seconds, then release. Repeat several times. Grip with your toes. Practice picking up an article of clothing with your toes, dropping it, and then picking it up again. Warm water. Soak your feet for 20 minutes in a bowl of warm water. Try doing the foot exercises while soaking, and also relax and rest your feet. Epsom salts. Add it to your warm foot bath soak.
Overpronation Of The Feet Treatment And Cause
Overpronation and underpronation describe general foot movements. These terms do not necessarily describe a medical problem with a foot. For example, you can overpronate and not have any problems or symptoms at all. It is important to have your foot structure and symptoms adequately assessed by your prescribing physician and a qualified practitioner. Once the underlying conditions and mechanical faults are assessed, an appropriate treatment plan including possible orthotic and footwear recommendations can be made.

Causes
There is a relationship between biomechanics and injury that is specific to each body part. Overall though, poor mechanics will either increase the landing forces acting on the body or increase the work to be done by the muscles. Both increase the stress, which, depending on the individual and the amount of running can become excessive and cause injury.
Symptoms
Because overpronation affects the entire lower leg, many injuries and conditions may develop and eventually cause problems not only in the leg and foot, but also the knee, hips and lower back. Pain often begins in the arch of the foot or the ankle. Blisters may develop on the instep, or on the inside edge of the heels. As overpronation continues and problems develop, pain will be felt elsewhere, depending on the injury.
Diagnosis
When sitting, an over-pronating foot appears quite normal, i.e. showing a normal arch with room under the underside of the foot. The moment you get up and put weight on your feet the situation changes: the arches lower and the ankle slightly turns inwards. When you walk or run more weight is placed on the feet compared to standing and over-pronation will become more evident. When walking barefoot on tiles or timber floors over-pronation is more visible, compared to walking on carpet or grass.

Non Surgical Treatment
Heel counters that make the heel of the shoe stronger to help resist/reduce excessive rearfoot motions. The heel counter is the hard piece in the back of the shoe that controls the foot?s motion from side-to-side. You can quickly test the effectiveness of a shoe?s heel counter by placing the shoe in the palm of your hand and putting your thumb in the mid-portion of the heel, trying to bend the back of the shoe. A heel counter that does not bend very much will provide superior motion control. Appropriate midsole density, the firmer the density, the more it will resist motion (important for a foot that overpronates or is pes planus), and the softer the density, the more it will shock absorb (important for a cavus foot with poor shock absorption) Wide base of support through the midfoot, to provide more support under a foot that is overpronated or the middle of the foot is collapsed inward.
Surgical Treatment
Subtalar Arthroereisis. The ankle and hindfoot bones/midfoot bones around the joint are fused, locking the bones in place and preventing all joint motion. This may also be done in combination with fusion at other joints. This is a very aggressive option usually reserved for extreme cases where no joint flexibility is present and/or the patient has severe arthritic changes in the joint.
What Exactly Is Severs Disease?
Although the name might sound pretty frightening, Sever's disease is really a common heel injury that occurs in kids. It can be painful, but is only temporary and has no long-term effects. Sever's disease, also called calcaneal apophysitis, is a painful bone disorder that results from inflammation (swelling) of the growth plate in the heel. A growth plate, also called an epiphyseal plate, is an area at the end of a developing bone where cartilage cells change over time into bone cells. As this occurs, the growth plates expand and unite, which is how bones grow. Sever's disease is a common cause of heel pain in growing kids, especially those who are physically active. It usually occurs during the growth spurt of adolescence, the approximately 2-year period in early puberty when kids grow most rapidly. This growth spurt can begin any time between the ages of 8 and 13 for girls and 10 and 15 for boys. Sever's disease rarely occurs in older teens because the back of the heel usually finishes growing by the age of 15, when the growth plate hardens and the growing bones fuse together into mature bone. Sever's disease is similar to Osgood-Schlatter disease, a condition that affects the bones in the knees.
Causes
Sever?s is often present at a time of rapid growth in adolescent athletic children. At this time the muscles and tendons become tighter as the bones become larger. Between 8 - 15 years of age is the usual onset of this condition.
Symptoms
Severs causes swelling, pain and tenderness over the back of the heel. Your child may walk with a limp. Initially the pain may be intermittent occurring only during or after exercise. As the problem gets worse, pain may be present most of the time. The swelling increases and is painful when touched or knocked. It commonly affects boys who are having a growth spurt during their pre-teen or teenage years. One or both knees may be affected.
Diagnosis
A doctor can usually tell that a child has Sever's disease based on the symptoms reported. To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor will probably examine the heels and ask about the child's activity level and participation in sports. The doctor might also use the squeeze test, squeezing the back part of the heel from both sides at the same time to see if doing so causes pain. The doctor might also ask the child to stand on tiptoes to see if that position causes pain. Although imaging tests such as X-rays generally are not that helpful in diagnosing Sever's disease, some doctors order them to rule out other problems, such as fractures. Sever's disease cannot be seen on an X-ray.
Non Surgical Treatment
See a doctor, who can diagnose the injury and recommend appropriate treatment options. It will be beneficial to rest the affected heel, and to regularly ice the affected area for the first few days. Anti-inflammatory pain medication can reduce pain and swelling, but first check with your doctor. As the pain diminishes a physical therapist can assist with a program of rehabilitation, incorporating stretching and strengthening exercises focused on the calf, shin and hamstring muscles. For a period after the injury has healed the doctor may advise on changes to your training routines that seek to lessen the strain on the heels. Orthotics are often recommended for your shoes in order to correct any biomechanical problems or lend extra support to the heels.
Exercise
Exercises that help to stretch the calf muscles and hamstrings are effective at treating Sever's disease. An exercise known as foot curling, in which the foot is pointed away from the body, then curled toward the body in order to help stretch the muscles, has also proven to be very effective at treating Sever's disease. The curling exercise should be done in sets of 10 or 20 repetitions, and repeated several times throughout the day.
Does Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction (PTTD) Always Involve Surgical Teatment ?
Overview
Posterior tibial tendon insufficiency (also called posterior tibial tendon dysfunction or adult acquired flatfoot) has been named literally after failure of the posterior tibial tendon. However, the condition is caused not only by the progressive failure of the posterior tibial tendon; it is also failure of associated ligaments and joints on the inner side of the ankle and foot. This results in collapse of the arch of the foot, along with the deformity which most often becomes the debilitating problem in its later stages. While at the beginning the common symptom is pain over the tendon in the inner part of the hindfoot and midfoot, later on it is the deformity that can threaten a person?s ability to walk. Just as the tendon degenerates and loses its function, other soft tissue on the same inner side of the foot - namely the ligaments - degenerate and fail. Ligaments are responsible for holding bones in place, and when they fail, bones shift to places where they shouldn?t; deformity is the result. The deformity causes malalignment, leading to more stress and failure of the ligaments. 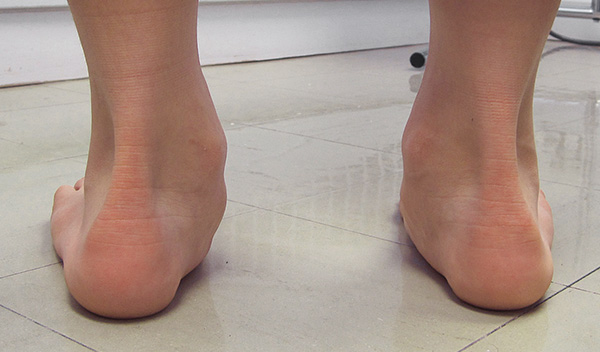
Causes
There are numerous causes of acquired Adult Flatfoot, including, trauma, fracture, dislocation, tendon rupture/partial rupture or inflammation of the tendons, tarsal coalition, arthritis, neuroarthropathy and neurologic weakness. The most common cause of acquired Adult Flatfoot is due to overuse of a tendon on the inside of the ankle called the posterior tibial tendon. This is classed as - posterior tibial tendon dysfunction. What are the causes of Adult Acquired flat foot? Trauma, Fracture or dislocation. Tendon rupture, partial tear or inflammation. Tarsal Coalition. Arthritis. Neuroarthropathy. Neurological weakness.
Symptoms
Pain and swelling around the inside aspect of the ankle initially. Later, the arch of the foot may fall (foot becomes flat), this change leads to walking to become difficult and painful, as well as standing for long periods. As the flat foot becomes established, pain may progress to the outer part of the ankle. Eventually, arthritis may develop.
Diagnosis
Your podiatrist is very familiar with tendons that have just about had enough, and will likely be able to diagnose this condition by performing a physical exam of your foot. He or she will probably examine the area visually and by feel, will inquire about your medical history (including past pain or injuries), and may also observe your feet as you walk. You may also be asked to attempt standing on your toes. This may be done by having you lift your ?good? foot (the one without the complaining tendon) off the ground, standing only on your problem foot. (You may be instructed to place your hands against the wall to help with balance.) Then, your podiatrist will ask you to try to go up on your toes on the bad foot. If you have difficulty doing so, it may indicate a problem with your posterior tibial tendon. Some imaging technology may be used to diagnose this condition, although it?s more likely the doctor will rely primarily on a physical exam. However, he or she may order scans such as an MRI or CT scan to look at your foot?s interior, and X-rays might also be helpful in a diagnosis.
Non surgical Treatment
Orthotic or anklebrace, Over-the-counter or custom shoe inserts to position the foot and relieve pain are the most common non-surgical treatment option. Custom orthotics are often suggested if the shape change of the foot is more severe. An ankle brace (either over-the-counter or custom made) is another option that will help to ease tendon tension and pain. Boot immobilization. A walking boot supports the tendon and allows it to heal. Activity modifications. Depending on what we find, we may recommend limiting high-impact activities, such as running, jumping or court sports, or switching out high-impact activities for low-impact options for a period of time. Ice and anti-inflammatory medications. These may be given as needed to decrease your symptoms. 
Surgical Treatment
Many operations are available for the treatment of dysfunction of the posterior tibial tendon after a thorough program of non-operative treatment has failed. The type of operation that is selected is determined by the age, weight, and level of activity of the patient as well as the extent of the deformity. The clinical stages outlined previously are a useful guide to operative care (Table I). In general, the clinician should perform the least invasive procedure that will decrease pain and improve function. One should consider the effects of each procedure, particularly those of arthrodesis, on the function of the rest of the foot and ankle.